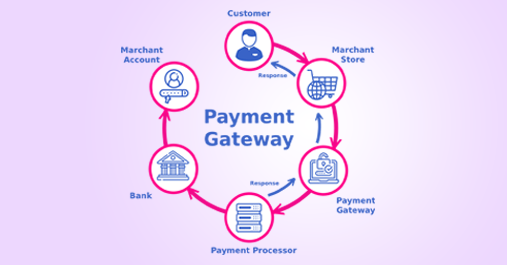
When an online payments service is coupled with an e-commerce platform, it functions as the channel via which customers can send and receive payments. This channel is known as a payment gateway.
Accepting payments involves the consumer is required to enter certain data, such as the number of their credit or debit card, the expiration date, and the CVV.
Following this step, the client will next make a payment, the funds for which will be sent from the buyer's account to the seller's (merchant's) account.
Digital Payment Process
Every time a payment is processed, the operation of an online payment gateway is controlled by a certain method.
A client purchases a service or product from a business using a payment gateway.
The payment gateway goes through several phases between the cardholder entering their information and the funds settling in the merchant's account.
- After placing the purchase online and proceeding to the payment page, the buyer must provide credit/debit card information.
- The card information is secured using Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption before being transferred between the browser and the merchant's web server.
- A payment gateway reduces the merchant's compliance requirements with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) without requiring clients to leave the website.
- The merchant then transmits transaction data to their payment gateway, an SSL-encrypted connection to the payment gateway's payment server.
- The payment gateway translates the XML message to ISO 8583 or a variant format (recognised by EFT Switches). It then transmits the transaction information to the payment processor used by the merchant's acquiring bank.
- The payment processor transmits the transaction details to the card association (Visa/MasterCard/American Express).
- Next, the credit card issuing bank gets the authorisation request, validates the available credit or debit, and then sends a response with a response code back to the processor (using the same method as for the authorisation) (i.e., approved or denied).
- The response code also communicates the cause for a failed transaction, such as insufficient money, etc.
- The processor then transmits the authorisation answer to the payment gateway, which transfers it to the payment processing interface.
- This method is known as Authorization or "Auth." This takes around 2-3 seconds to complete.
- The merchant then fulfils the order, and the preceding steps may be repeated to "Clear" the authorisation by completing the transaction.
- Clear is often triggered only after the merchant has completed the transaction (I.e. shipped the order).
- This causes the issuing bank to "clear" the authorisation (i.e., convert the authorisation hold to a debit) and prepares them to settle with the merchant acquiring bank.
- The merchant sends all accepted authorisations in a "batch" (at the end of the day) to their acquiring bank's processor for settlement.
- Typically, this decreases or "Clears" the relevant "Auth" if it has not already been "Cleared" expressly.
- The acquiring bank submits a batch settlement request to the credit card user.
- The credit card issuer pays a settlement payment to the acquiring bank as the eleventh step (the next day in most cases).
- The acquiring bank then transfers the number of authorised monies to the merchant's designated account (the same day or the next day).
International Payment Gateway Information
Although the company expands internationally, you sell in a variety of currencies. When customers see a company's expenses in terms of their money, they are more likely to adopt anything new. International buyers can pay according to their currency through a global payment platform.
Payment systems have even less impact on foreign payments, but they make transactions go even more efficiently.
Information about Payment Gateway Services
A payment gateway software allows businesses to receive checking accounts or bill payments through clients. This term encompasses physical badge systems and payment processing interfaces used by retailers.
Providers of Payment Gateway Services
How much you'll need to receive payments securely and effectively is critical for millions of businesses accepting payments. It is necessary to manage a business that offers a product as per a Reserve Bank analysis dated 2020. Contactless accounts account for about 74% of purchases. As more customers can easily switch to another income, these transaction tendencies may keep expanding. Let's look at what a payment service provider is, how it works, and the advantages of using one.
Retailers may accept online currencies with the assistance of something like a payment provider. PSPs manage this same transaction history transaction through coordination between retailers, and institutions, including payment providers. The payment process explains in the subsequent instance.
Payment Gateway Systems
The technology which receives but instead transmits billing information from a consumer to something like a trader's bank statement is characterised as a payment platform. Its role is to collect data, confirm if resources are sufficient, and pay a retailer. A payment processor is an internet system that links customers and businesses over the network.
Conclusion
Payment gateways are a crucial component of the digital economy. By allowing consumers to communicate their credit card information safely and securely, these solutions alleviate some obstacles to online shopping. Payment gateways have evolved from basic card-reading devices to complex systems that gather and validate PINs, signatures, and other information for merchant transactions.

 Careers
Careers About US
About US  Blog
Blog  News
News FAQ's
FAQ's Policy
Policy